Intro to Agentic Architecture
Agentic AI, also known as Autonomous AI, represents a sophisticated form of artificial intelligence designed to replicate human decision-making processes. It focuses on goal setting, plan generation, and adaptability to new data or feedback. Agentic AI can:
- Make Independent Decisions: Based on its understanding of the environment and objectives.
- Take Initiative: Actively seek opportunities or address challenges.
- Learn and Adapt: Continuously improve performance through experience.
- Exhibit Goal-Oriented Behavior: Pursue specific outcomes dynamically.
This cognitive AI system reasons, learns, and adapts, enabling it to deconstruct complex problems, organize tasks, and achieve goals autonomously. Core principles include autonomy, adaptability, and feedback.
Key Features of Agentic AI
- Autonomy: Operates independently, reducing reliance on human intervention.
- Adaptability: Adjusts to new information and evolving environments.
- Real-Time Learning: Continuously refines strategies for decision-making.
- Scalability: Handles growing complexity using distributed computing and cloud infrastructures.
- Interoperability: Seamlessly integrates with existing technologies and systems.
- Lease or Build: Offers flexible implementation options tailored to organizational needs.
Sample Agents in Industry
Retail and E-commerce
- Inventory Optimization Agent: Analyzes sales trends, predicts demand, and automates restocking to reduce overstock and stockouts.
- Customer Support Agent: A chatbot that handles common customer inquiries, processes returns, and provides personalized product recommendations.
- Dynamic Pricing Agent: Adjusts pricing based on market trends, competitor pricing, and customer demand.
- Personalized Marketing Agent: Crafts targeted campaigns based on customer behavior and purchase history.
Healthcare
- Appointment Scheduling Agent: Automates patient bookings, reminders, and follow-ups.
- Diagnostic Assistance Agent: Analyzes patient symptoms and suggests potential diagnoses for further review by professionals.
- Compliance Monitoring Agent: Ensures adherence to medical regulations and documentation standards.
Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance Agent: Monitors machinery and predicts failures to minimize downtime.
- Quality Assurance Agent: Uses computer vision to detect defects in products on the production line.
- Supply Chain Optimization Agent: Streamlines procurement, inventory, and logistics for cost and time efficiency.
Agriculture
- Crop Health Monitoring Agent: Utilizes drone and satellite data to assess crop conditions and suggest interventions.
- Irrigation Optimization Agent: Analyzes soil moisture, weather patterns, and crop needs to optimize water usage.
- Yield Prediction Agent: Predicts harvest outcomes based on environmental and operational data.
Real Estate
- Property Valuation Agent: Uses market data to provide accurate property valuations.
- Lead Management Agent: Automates engagement with potential buyers and sellers, scheduling viewings and follow-ups.
- Smart Building Management Agent: Controls energy usage, lighting, and security systems in commercial properties.
Legal
- Contract Review Agent: Identifies risks and highlights key terms in contracts.
- Legal Research Agent: Quickly retrieves relevant case laws and precedents.
- Compliance Tracking Agent: Monitors regulatory updates and ensures compliance.
Media and Entertainment
- Content Recommendation Agent: Suggests tailored content for individual users.
- Creative Assistant Agent: Helps generate ideas for campaigns, scripts, or artwork.
- Audience Analytics Agent: Provides insights into viewer preferences and behavior.
Education
- Adaptive Learning Agent: Personalizes educational content based on student performance and learning pace.
- Administrative Support Agent: Automates enrollment, grading, and reporting processes.
- Student Support Agent: Provides round-the-clock assistance for students with queries about courses or administrative tasks.
Food and Beverage
- Recipe Optimization Agent: Suggests ingredient substitutions and cost-saving measures while maintaining quality.
- Order Prediction Agent: Forecasts customer orders for efficient preparation and resource allocation.
- Food Safety Monitoring Agent: Tracks compliance with health and safety regulations.
Professional Services
- Client Relationship Management Agent: Keeps track of client interactions and sends reminders for follow-ups.
- Proposal Drafting Agent: Automates the creation of project proposals based on client requirements.
- Billing and Invoicing Agent: Handles payment tracking and invoice generation.
Energy and Utilities
- Energy Efficiency Agent: Optimizes energy consumption based on usage patterns and external conditions.
- Grid Monitoring Agent: Tracks and predicts grid performance to reduce outages.
- Renewable Resource Optimization Agent: Manages the integration of renewable energy sources.
Finance and Accounting
- Fraud Detection Agent: Monitors transactions for suspicious activities.
- Cash Flow Forecasting Agent: Predicts financial trends to aid in decision-making.
- Tax Compliance Agent: Ensures accurate filing and compliance with tax regulations.
Hospitality
- Guest Experience Agent: Personalizes guest interactions, such as room preferences and activity suggestions.
- Booking Management Agent: Automates reservations and overbooking management.
- Feedback Analysis Agent: Analyzes reviews and feedback to identify improvement areas.
Construction
- Project Timeline Agent: Tracks progress and predicts delays in construction projects.
- Cost Estimation Agent: Provides detailed cost breakdowns for projects.
- Safety Monitoring Agent: Uses IoT sensors and AI to ensure compliance with safety standards on-site.
Transportation and Logistics
- Route Optimization Agent: Suggests efficient delivery routes to save time and fuel.
- Fleet Management Agent: Monitors vehicle health, schedules maintenance, and tracks driver performance.
- Cargo Tracking Agent: Provides real-time updates on the location and condition of shipments.
Sample Agentic Scaffolding Architecture
- Input Layer: Sources like live data streams and interaction logs.
- Agent Orchestration: Adaptive task management and system supervision.
- Agents: Capabilities like planning, reflection, and self-learning.
- Output Layer: Tailored results and knowledge updates.
- Service Layer: Multi-channel delivery and intelligent recommendations.
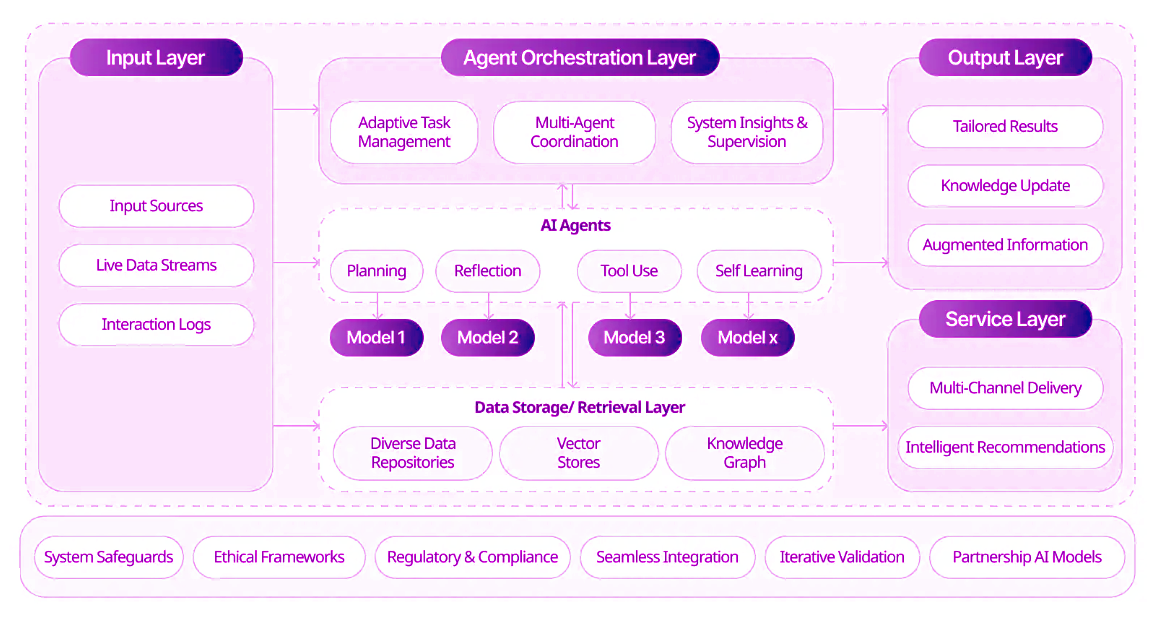
Sample Agent Technical Design
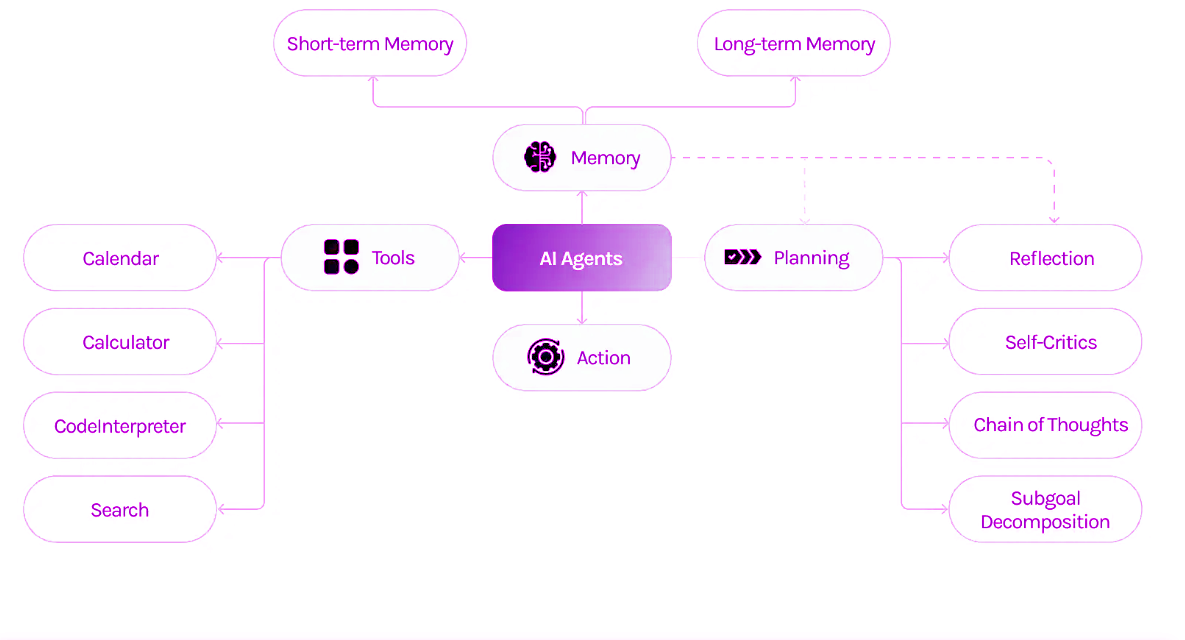
More Details regarding AI Agents
Agentic AI Leverageable Technologies
- Machine Learning: Algorithms for learning and improving performance.
- Deep Learning: Neural networks for tasks like image recognition and NLP.
- Computer Vision: Processing visual data to understand scenes and objects.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enabling interaction through human language.
- Robotics: Designing and operating robots for physical tasks.
- Planning and Decision-Making: Algorithms for goal-oriented actions.
- Simulation and Modeling: Testing in simulated environments.
Agent Types
- Vertical Agents: Focused on specific domains or tasks.
- Horizontal Agents: Broad application across multiple areas.
- Multi-Modal Agents: Combining inputs like text, images, and audio.
- Interface Agents: Enhancing user interactions.
Pricing Models
- Platform: Charges based on platform access.
- Service: Charges based on specific services.
- Outcome-Based: Charges based on results achieved.
- Combinations: Hybrid approaches blending different models.
Best Practices for Implementing Agentic AI
- Define Objectives: Set clear goals and measurable targets.
- Data Collection: Gather and analyze relevant data.
- Model Development: Select algorithms and train models.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporate AI into workflows.
- Monitoring: Continuously evaluate and optimize performance.
- Collaboration: Foster interdisciplinary cooperation between teams.
- Ethical Considerations: Align development with ethical guidelines.
Challenges in Agentic AI Systems
- Cost: High initial and operational costs.
- Reliability: Ensuring traceability, human-in-the-loop interventions, and real-time monitoring.
- Complexity Management: Modular designs to address complexity.
- Transparency: Explainable and understandable decisions.
- Trust and Reliability: Mitigating unpredictability in high-risk scenarios.
- Ethical Implications: Reducing biases and aligning with human values.
- Compliance and Privacy: Adhering to regulations and ensuring data security.
- Cultural Resistance: Overcoming resistance to adoption.
- Success Metrics: Establishing measurable performance benchmarks.
- Buy vs Build: Determining cost-effectiveness and scalability.
The Role of Memory and Context Window Size in Agent Adoption
Enhanced memory and extended context window sizes play a crucial role in enabling businesses to adopt agents effectively. Key benefits include:
- Improved Decision-Making: Longer context windows allow agents to process and analyze extensive data, leading to more informed and accurate decisions.
- Enhanced Learning: Increased memory capacity enables agents to retain and utilize a broader history of interactions, improving adaptability and performance.
- Better Task Management: Agents can handle complex, multi-step tasks by maintaining continuity and coherence across longer interactions.
- Seamless Integration: Extended context windows facilitate better integration with interconnected systems, leveraging historical data for consistency.
- User Experience: By reducing redundancy in user interactions, agents provide smoother, more intuitive responses and recommendations.